Parkinson’s Disease: Early Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Parkinson’s Disease: Early Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
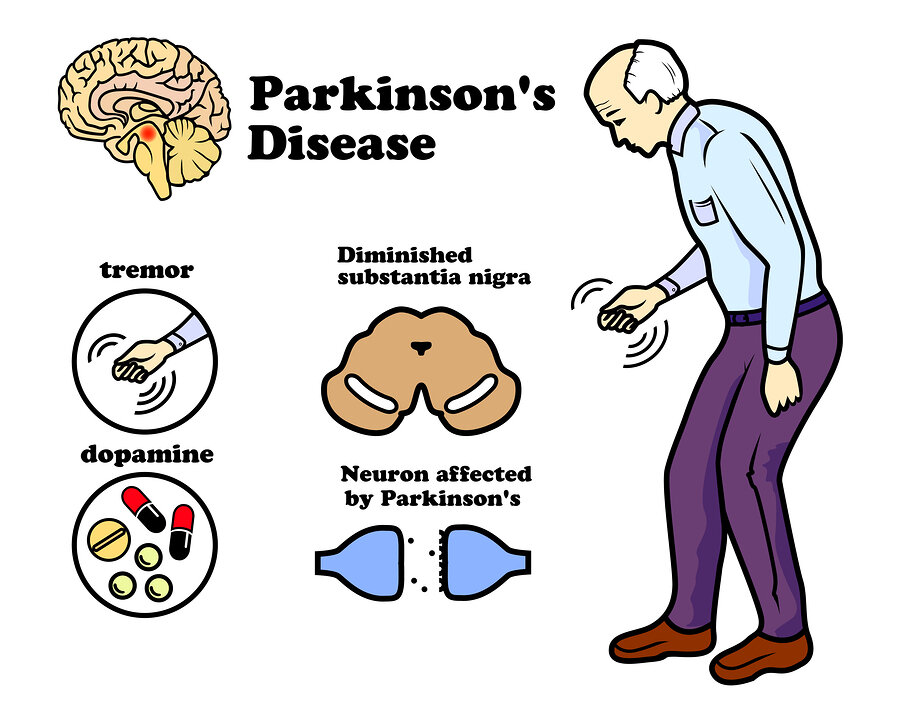
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement. It usually develops after the age of 60, although early-onset cases can occur. Understanding the early symptoms and seeking timely medical care can help manage the condition effectively and improve quality of life.
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disease occurs when certain nerve cells in the brain responsible for producing dopamine gradually degenerate. Dopamine is a chemical that plays a key role in controlling smooth and coordinated muscle movements. When dopamine levels decrease, individuals begin to experience tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with movement.
Early Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
Common early symptoms include:
- Slight tremor in one hand, finger, or chin
- Slowness of movement
- Muscle stiffness or rigidity
- Reduced facial expressions
- Softer or slower speech
- Changes in handwriting (smaller writing)
- Balance or posture problems
- Reduced sense of smell
- Sleep disturbances
- Constipation or mood changes such as anxiety or depression
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is not fully known, but several factors may increase the risk:
- Age: Risk increases with advancing age
- Genetics: A family history may slightly increase susceptibility
- Environmental exposure: Long-term exposure to certain toxins or chemicals
- Brain changes: Loss of dopamine-producing nerve cells and abnormal protein accumulation in the brain
Diagnosis
There is no single test that confirms Parkinson’s disease. Diagnosis is mainly based on:
- Medical history and symptom evaluation
- Neurological examination
- Assessment of movement-related symptoms
- Imaging tests when needed to rule out other conditions
Treatment and Management
Although Parkinson’s disease currently has no permanent cure, several treatment approaches can help manage symptoms and improve daily functioning.
Management strategies include:
- Medications that help improve movement control
- Regular physical exercise to maintain mobility and balance
- Physiotherapy and occupational therapy to support daily activities
- Speech therapy for voice and swallowing difficulties
- Healthy diet, adequate sleep, and stress management
- Advanced therapies or surgical options in selected cases when required
When to Consult a Doctor
Consult a healthcare professional if persistent tremors, stiffness, slowed movements, or unexplained balance problems are noticed. Early diagnosis allows better symptom management and helps maintain independence for a longer period.
Conclusion
Parkinson’s disease is a long-term neurological condition, but with early detection, proper treatment, rehabilitation, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can continue to lead active and fulfilling lives. Awareness of early symptoms and timely medical consultation play a vital role in managing the disease effectively.
Check this also:
- Who is the Best Neurologist in Faridabad City?
- Best Neurologist for Seizure Treatment in Faridabad
- What Are Usually the Early Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease?
- Frequent Headaches and Dizziness: Types, Causes & Treatment